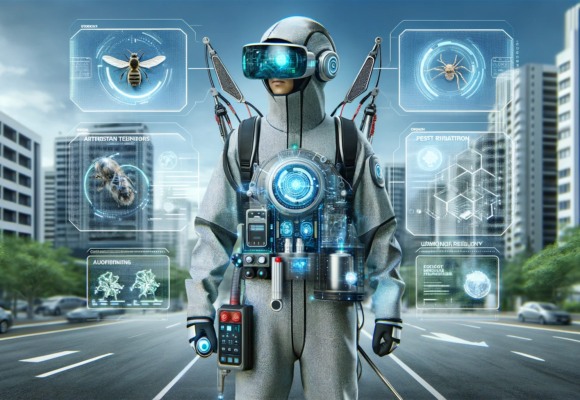
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into insect and pest control businesses globally is transforming the industry by enhancing efficiency, effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. AI technologies offer innovative solutions to age-old problems of pest management, ranging from agriculture to urban settings. Here’s a summary of the significant effects of AI on insect and pest control:
Enhanced Detection and Identification:
- Automated Monitoring Systems: AI-powered cameras and sensors can continuously monitor environments for signs of pest activity, identifying specific species with high accuracy. This real-time detection allows for immediate action and can significantly reduce the extent of infestations.
- Image Recognition Technology: AI algorithms trained on vast datasets can analyze images from traps or monitoring devices to identify pests. This capability facilitates early detection and helps in determining the most effective control strategies for specific pest types.
Precision Pest Management:
- Targeted Treatment Solutions: By accurately identifying pests and assessing their population levels, AI enables more targeted pest control measures. This precision reduces the need for broad-spectrum pesticides, minimizing chemical usage and environmental impact.
- Drone and Robot Deployments: AI-equipped drones and robots can apply pesticides or biological control agents precisely where needed, reducing waste and exposure to non-target species. These technologies can access difficult-to-reach areas, improving treatment coverage and effectiveness.
Predictive Analytics:
- Pest Population Forecasting: AI models can predict pest outbreaks by analyzing data on weather patterns, crop types, and historical pest activity. This predictive insight allows businesses and farmers to implement preventative measures in advance, potentially avoiding significant losses.
- Resistance Management: AI can help in tracking and predicting the development of pest resistance to pesticides, guiding the rotation of control methods to maintain their effectiveness over time.
Sustainable and Eco-friendly Practices:
- Reduced Chemical Use: By enabling more accurate and targeted applications, AI contributes to the reduction of chemical pesticides, favoring more sustainable practices like biological control and integrated pest management (IPM) strategies.
- Biodiversity Protection: Precise pest control methods guided by AI help protect non-target species and preserve biodiversity, addressing one of the major environmental concerns associated with traditional pest control methods.
Business Efficiency and Compliance:
- Operational Efficiency: AI-driven automation of monitoring and control processes reduces labor costs and enhances the efficiency of pest control operations, allowing businesses to scale their services more effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance: AI tools can help businesses stay compliant with local and international regulations regarding pesticide use and environmental protection by ensuring that only necessary and approved substances are applied.
Challenges and Considerations:
- High Initial Investment: Implementing AI technologies requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and training, which may be a barrier for small to medium-sized enterprises.
- Data Privacy and Security: The collection and analysis of environmental and pest-related data raise concerns about privacy and data security that businesses need to address.
- Technological Adaptation: The success of AI in pest control depends on the willingness and ability of businesses and workers to adapt to new technologies and methods.
In conclusion, AI’s impact on the insect and pest control industry is profound, offering revolutionary approaches to detection, identification, and management of pest populations. These technologies promise to enhance the effectiveness of pest control measures, reduce environmental impact, and improve the sustainability of practices. However, realizing these benefits on a global scale requires overcoming challenges related to investment, data security, and technological adaptation.


 21 Feb 2024
21 Feb 2024
 Posted by Watchdog Ent.
Posted by Watchdog Ent.  0 Comment
0 Comment