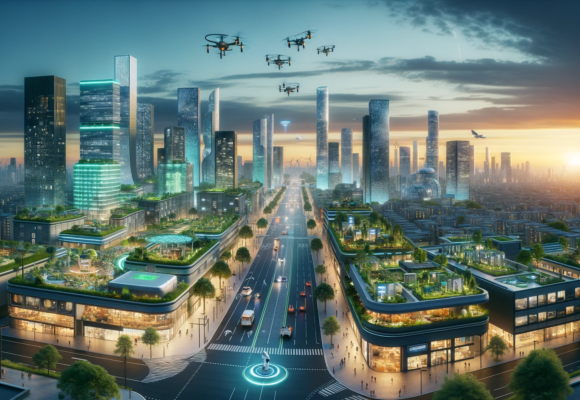
Over the next two decades, artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to play a pivotal role in enhancing sustainability within major cities globally. As urban populations continue to grow, the imperative to create more efficient, livable, and sustainable urban environments has never been greater. AI offers an array of solutions to tackle these challenges by optimizing resource use, improving environmental quality, and enhancing public services. Here’s a summary of the significant impacts AI is expected to have on urban sustainability:
Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Integration
AI will revolutionize the energy sector by making it more efficient and sustainable. Smart grids, powered by AI, will optimize the distribution and use of electricity, reducing waste and ensuring that energy supply matches demand in real-time. AI will also facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources into the power grid, predicting fluctuations in solar and wind energy production and adjusting grid operations accordingly to minimize reliance on fossil fuels.
Sustainable Urban Mobility
AI will transform urban mobility by optimizing traffic flow, reducing congestion, and lowering emissions. Intelligent transportation systems, using AI algorithms, can manage traffic lights and public transportation routes to improve efficiency. Furthermore, AI will be instrumental in the development and adoption of autonomous electric vehicles, reducing the carbon footprint of urban transport and making it safer and more accessible.
Waste Management and Recycling
AI can significantly improve waste management processes in cities, leading to higher recycling rates and less landfill use. By analyzing data on waste generation patterns, AI can optimize collection routes and schedules, reducing emissions from waste collection vehicles. AI-powered sorting systems in recycling facilities can more accurately separate materials, increasing the efficiency of recycling and the quality of recycled materials.
Water Conservation and Management
AI technologies will enhance water conservation efforts and reduce waste by detecting leaks in water distribution networks in real-time, significantly reducing water loss. Additionally, AI can optimize water treatment processes, ensuring that water is used and recycled efficiently, which is crucial for water-scarce regions and growing urban populations.
Air Quality Monitoring and Improvement
AI will play a key role in monitoring and improving air quality in major cities. By analyzing data from a network of sensors, AI can identify pollution sources and patterns, enabling targeted interventions. Cities can use AI predictions to issue warnings, regulate traffic, and enforce environmental regulations more effectively, leading to cleaner air and healthier urban environments.
Urban Planning and Green Spaces
AI will contribute to more sustainable urban planning by analyzing vast amounts of data on land use, human activity patterns, and environmental factors. This can inform the development of green spaces, sustainable buildings, and infrastructure projects that enhance the quality of life while minimizing environmental impact. AI can also help monitor and manage the health of urban green spaces, ensuring they provide maximum ecological benefits.
Challenges and Governance
The deployment of AI in enhancing urban sustainability will require careful governance to ensure ethical use, data privacy, and security. Cities will need to develop frameworks for the responsible use of AI, involving stakeholders in the process to address social, economic, and environmental considerations equitably.
Conclusion
In the next 20 years, AI is set to be a transformative force for sustainability in major cities worldwide. By optimizing resource use, enhancing efficiency, and enabling informed decision-making, AI can help cities meet their sustainability goals, improving the quality of life for urban residents. However, realizing this potential will require strategic investment, cross-sector collaboration, and a commitment to ethical and equitable technology deployment.


 15 Feb 2024
15 Feb 2024
 Posted by Watchdog Ent.
Posted by Watchdog Ent.  0 Comment
0 Comment